Automotive relays are electrically operated switches that control circuits using power from another source, such as a switch, computer, or control module. These relays automate power distribution, enabling circuits to turn on and off at specific times. However, their true advantage goes beyond automation—they allow for the control of multiple circuits, including those with different voltage types, within the same relay simultaneously.
Why Are Automotive Relays Important?
12V DC relays are essential for full-voltage applications, as they enable a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. This functionality is crucial for various automotive components, including:
- Horns
- Headlights
- Auxiliary lamps
- Fan motors
- Blower motors
- Other high-power vehicle equipment
By utilizing relays, vehicles can efficiently manage electrical loads, ensuring safety and longevity for critical automotive systems.
How Is a Relay Designed?
- Electromagnetic Coil – Generates a magnetic field when current flows through it.
- Switch (Contacts) – Moves between open and closed positions to control the circuit.
- Spring – Holds the switch in position until the coil is energized.
When the coil is activated, the magnetic field moves the switch, opening or closing the circuit.
Understanding Relay Pin Numbers
Most 12V relays follow a standard pin configuration:
- 85 & 86: Coil pins that transfer current through the coil. One pin connects to the ground, while the other connects to the power source.
- 30: Common terminal, which connects to the battery power source.
- 87 & 87a: Output terminals:
- 87a (Normally Closed – NC): Connected to 30 when the relay is off.
- 87 (Normally Open – NO): Connects to 30 when the relay is activated
How to Wire an Automotive Relay
- Identify the Pins:
- Locate pin 30 (power input) perpendicular to the other pins for easy identification.
- Ensure that 85 and 86 are correctly wired to transfer current through the coil.
- Connect the Power Source:
- Pin 30 should connect to the battery.
- One of the coil pins (85 or 86) should be grounded.
- Wire the Controlled Accessories:
- If using a Normally Open relay, connect the accessory to pin 87.
- If using a Normally Closed relay, connect the accessory to pin 87a.
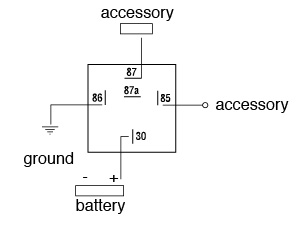
By following this wiring approach, you can ensure your relay efficiently controls the intended electrical component.
Types of Automotive Relays
There are various types of automotive relays, each serving specific applications:
- Change-Over Relay – Allows switching between two circuits.
- Normally Open Relay – Activates when the coil is energized.
- Potted Relay – Sealed for protection against harsh environments.
- Flasher Relay – Controls flashing signals like turn signals.
- Skirted Relay – Designed for secure connections in OEM applications.
- Time Delay Relay – Introduces a delay before switching the circuit.
- Dual Open Contact Relay – Controls two independent circuits simultaneously.
For an in-depth look at these relay types, check out our guide on Types of Relays Explained.
Final Thoughts
Automotive relays play a vital role in managing electrical systems, ensuring efficiency, safety, and longevity. Whether you’re wiring headlights, fan motors, or auxiliary lamps, understanding how relays function and how to wire them properly is crucial.
If you need assistance selecting the right relay for your application, visit www.delcity.net or call 1.800.654.4757 to speak with an expert.